Usage and Handling
- In using a lead, a switch, a relay, a motor driver IC, and the like, give due consideration in capacitance and heat resistance. In case they do not meet proper standards, this leads to a failure such as a burnout.
- Confirm and assure the matching and the reliability of the motor on actual set or unit application.
The examples of the confirmation on actual set are:
The reliability, electric characteristics, mechanical characteristics, mechanical/electric noise, environmental storage, influence from atmosphere/gas etc.
- The internal resistance of the motor driving power source (containing an electrical circuit) and use of the motor with high/low voltage, high current, and pulse-driven (including PWM) affect the life span of the motor and starting ability. When the temperature deviates from the normal room temperature as is the case in low and high temperature situations, please note the conditions.
- Short circuit between terminals due to end of motor life or short circuit between commutator slits due to specific environmental/use conditions might occur. In order to prevent circuit burnout, take protective measures such as using fuses.
- The longer you use the motor, the lower its insulation resistance becomes. Therefore, be careful in using housing/endbell and power supply GND in common.
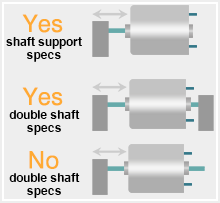
- Axial thrust on the output shaft could have an adverse effect on the motor life. i. e. As is produced by worm gears, fans, etc., Check the service life expected under the actual operating conditions by testing the motors installed in your application products. For heavy thrust loads, consider using something mechanical to retain the shaft end. Otherwise, this might cause any problem in contact.
- In using any transmission system such as a belt drive system for an output shaft, with which radial load is applied to the motor, sufficiently note that the life of the motor might be shortened due to the radial load applied to the bearing.
- Motor life may be affected adversely by heavy radial load such as produced by rotating eccentric cams, etc., and also by vibration given from outside. DO check over such negative factors by testing the motors to the actual operating conditions in your application products.
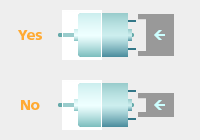
- When press fitting a pulley, gear etc., onto the motor output shaft, always support the shaft at the other end or its retaining metal pad in a proper and correct way.
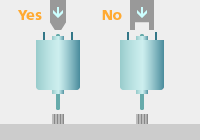
- In pressing the motor into any cylindrical case, press the outer peripheral part of the housing/endbell.
Intensive pressure on any part near the center of the endbell might cause starting disability of motor. So please take care for motor mounting not to push the part. Specifically, be careful about any small-diameter motor, since its speed (rpm) changes depending on the fixing force.
- In fixing the motor, do not apply any force that deforms the body of the motor. Also, in screwing the motor, do not screw it unevenly. This might adversely affect the flatness or characteristics of the motor mounting surface.
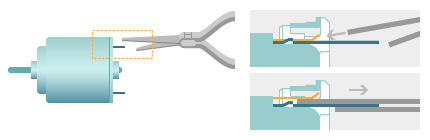
- Do not apply any force that presses into, pulls, or bends the motor terminal. Since RE type terminal is based on Mabuchi's unique snap-in terminal system, it is removable. Generally terminals are not removed. In case it becomes necessary to remove any terminal, however, remove the terminal using the tool shown in the figure below taking care not to damage the brush.
- When mounting your motors by means of binding agents, DON'T allow any adherence to the bearings nor intrusion into the motors.
- In using a large amount of oil or grease, also be careful and prevent the oil or the grease from flowing in the motor. The inflow might cause a failure such as defective starting.
- If mounting the motor and assembling the unit, equipment which emits ultrasonic waves is used there is a danger that some of the internal parts of the motor might be damaged so please take care.
- When soldering, BE SURE to finish your work quickly so as not to develop thermal plastic deformation around the motor terminals nor to give them any forced bend or inward depression. In doing so, special care must be taken not to allow solder debris and flux to spatter into motors and precautionary measures should be taken if necessary, by covering up all the nearby holes and apertures. Any motors having snap-in terminals must also be attended carefully so as not to get flux in along the terminals, as it may cause failure in electrical conduction.
- Do not touch the motor bearing. It might absorb bearing oil and cause bearing noise.
- Identification marking drawn on motor housing with dyestuff marker may be blurred or may fade out when rubbing.